Autoimmune diseases can range from being common to rare, but unfortunately many of them do not have effective treatments or cures. Can CBD oil be the answer for all those suffering with these diseases?
What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
It is thought that over 14 million Americans are diagnosed with an autoimmune disease. So, what are these diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are certain diseases that result from a dysfunction in the immune system. These occur when the immune system starts attacking the body’s own cells, instead of attacking foreign cells that are causing harm to the body like it usually does. When the body starts attacking itself, it can break down organs and cause various problems, depending on the organ.
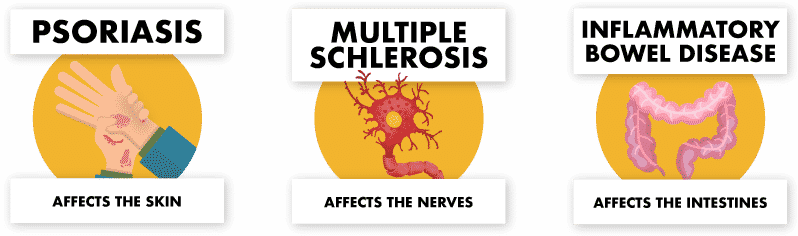
Some of the most common autoimmune disorders include lupus, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBS), and type 1 diabetes (T1DM). Other examples include multiple sclerosis (MS) and myasthenia gravis (MG). These diseases can have different signs and symptoms based on the organs that are affected. For example, psoriasis affects the skin and deals with skin-related problems, while another type of disease like IBS affects the intestines and has digestive tract related problems.
How Are Autoimmune Diseases Diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be a difficult task since they often present as other non-autoimmune diseases. However, most start with fatigue and a low-grade fever. Along with that, one of the classic signs of autoimmune diseases is inflammation. Inflammation can present as redness, swelling, pain, soreness, or heat. Depending on the type of disease, the other signs and symptoms vary.
There are some blood tests that physicians can run to help them narrow down the options. These include tests such as the Antinuclear Antibody Test (ANA) or autoantibodies test. Another way to check is to look for markers of inflammation such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). If any of these are abnormal, it can help guide the physician in their diagnosis.
What Causes Autoimmune Disease?
As you can see, autoimmune diseases can take place in a variety of forms. But is there a common mechanism behind all of them?
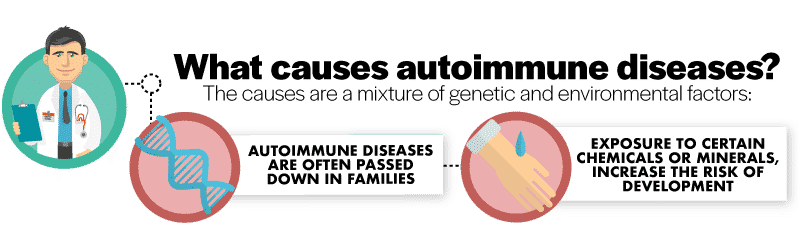
Even though autoimmune diseases are becoming more prevalent, the causes of them are still mostly unknown. The most widely believed opinion is that they are caused by a mixture of genetics and the environment. This means that if your family members have an autoimmune disease, you are more likely to have one as well. It also means that certain environmental factors, such as being exposed to certain chemicals or minerals, can increase your risk of developing the disease. Interestingly enough, gender may also play a role as more women are diagnosed with autoimmune disorders than men.
Once the autoimmune disease develops, the proposed theory is that the body’s immune system creates autoantibodies that set out to destroy the healthy cells in the body. Normally, antibodies attack foreign cells that are causing an infection or damage to the body. As these autoantibodies start to injure tissues and organs, the autoimmune disease becomes more present and the signs and symptoms start to become noticeable.
What Role Does Inflammation Play?
Inflammation plays a key role when the immune system starts attacking cells. Inflammation can cause the blood vessels to widen and lets more blood rush to the area of attack, which leads to the heat and redness that are signs of inflammation. The blood carries certain mediators, like bradykinin and histamine, which help destroy the harmful agents that the immune system sets out to attack. They also assist with healing the body. These mediators can sometimes cause irritation – which sends pain signals to the brain. This is why we sometimes feel pain or soreness when a part of the body is inflamed. However, the mediators also allow the blood vessels to become more permeable (i.e. things can flow in and out of the vessels easier), which permits more defense mediators to come and help fight. Often times, they bring fluid along with them which causes the swelling associated with inflammation.
In autoimmune diseases, this inflammation is usually a chronic inflammation instead of temporary, as it is with infections. Short term inflammation is actually good for the body since it helps fight off infections. Chronic inflammation, however, can damage DNA and even cause internal scarring. Many people link chronic inflammation to other health issues such as heart disease, cancer, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
How Can CBD Help?
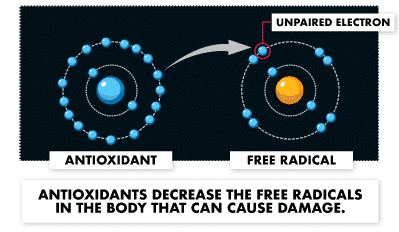
Since many people contribute the problems associated with autoimmune disorders to inflammation, the idea is that CBD can help with these diseases due to its anti-inflammatory properties. In the 90’s, a study proposed that CBD is more potent, in terms of antioxidant properties, than other antioxidants such as vitamin E or vitamin C. Antioxidants help reduce inflammation because they decrease the number of free radicals that cause damage to the body.
Another study in mice showed that CBD can reduce TNFα, which is a protein that stimulates inflammation in the body. TNFα is commonly used as a marker for measuring inflammation. So, if TNFα is decreased, inflammation is decreased as well.
It is thought that CBD does not produce its anti-inflammatory effects through the same mechanism as traditional anti-inflammatory drugs such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Typical NSAIDs are ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve). This means that CBD may be able to produce similar effects but without the side effects associated with long-term use of NSAIDs, like gastrointestinal (GI) ulcers and bleeding.
So, how does CBD produce its anti-inflammatory effects?
The exact mechanism is still being researched. One theory involves the A2A receptor, which is an adenosine receptor. Adenosine promotes anti-inflammatory actions in the body. CBD is thought to increase the effects of adenosine, which decreases inflammation. Another theory involves glycine receptors. Glycine receptors deal with pain in the spine and relates to pain and inflammation of the nerves. Nerve pain is usually described as tingling, burning, or shooting pain. Many think that inflammation around the nerves causes nerve pain. Therefore, CBD may suppress inflammation (and nerve pain) through acting on the glycine receptors.
What Does the Research Say?
Due to the wide variety of autoimmune disease, this article only focuses three specific autoimmune diseases: psoriasis, lupus, and MS. The next section goes into more detail about the studies that were researched for these diseases. However, the inflammation research described in the section above applies to all autoimmune diseases.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a type of autoimmune disease that affects the skin. It is thought to be caused by inflammation as well as hyper-proliferation (aka rapid buildup) of skin cells. Basically, the production of skin cells is sped up in people with psoriasis, and the cells do not fall off the skin in a normal fashion. Therefore, extra skin cells accumulate on top of the skin. This buildup of skin cells leads to scaling of the skin that present as dry, red patches. These patches typically develop on the joints, such as the knees or elbows.
Most current research for psoriasis and CBD has only been in cell culture and not in humans. However, the research in cell culture is promising because it shows that CBD helps psoriasis by two mechanisms: decreasing inflammation and decreasing new skin cell growth, therefore decreasing buildup of skin cells. Additionally, the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD) released a statement in early 2018 mentioning that because of the anti-inflammatory properties of cannabis, “there may be potential for topical cannabis to improve conditions such as acne, psoriasis and eczema by reducing the inflammation associated with these diseases”. They also stated that more research on topical use of cannabis products needs to be performed since the popularity of topical products has grown.

Lupus
Unlike some other autoimmune diseases, lupus can affect the whole body. This includes the skin, joints, lungs, kidneys, and other organs. Lupus is hard to diagnose because the symptoms often are similar to other problems. However, it is often associated with a rash on the face, known as the “butterfly rash” due to its shape. But not all lupus cases include the rash. People with lupus can have “flares” when the signs and symptoms suddenly increase and then these symptoms disappear or at least get better for a while. Lupus can be triggered by infections, sunlight, and even certain medications.
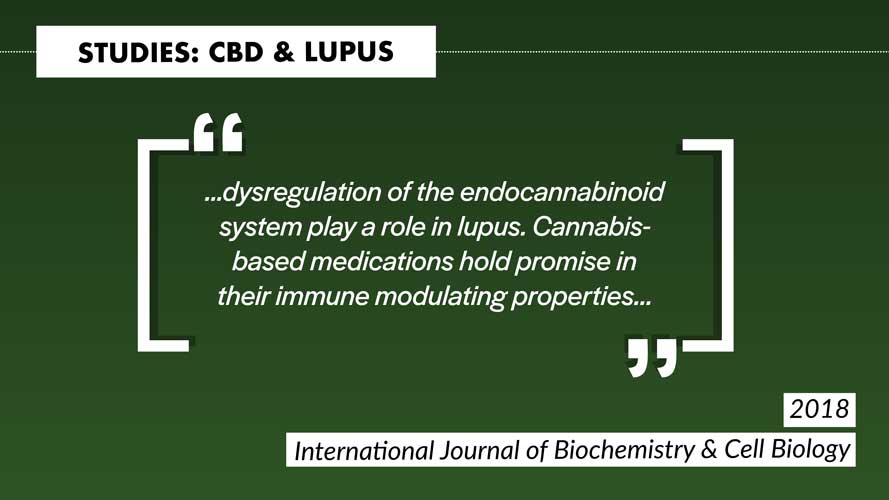
The research is pretty scarce for lupus and CBD. Most studies are trying to relate the endocannabinoid system to lupus and research shows that one endocannabinoid, 2-AG, seems to play a role in the mechanism behind lupus. However, one recent study suggests that CBD may actually worsen lupus by increasing kidney damage in mice. Although, this is only one study and only the abstract is available as of now. Once the full article is available, we might have some more clarification in terms of how impactful this study will be. Of course, there is no current data in humans, so it is hard to say for sure if this finding is true. It is best to exercise caution when using CBD with lupus, and always talk with a healthcare provider about your treatment options.
Multiple Sclerosis
MS is a type of autoimmune disease that attacks the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the spine, the brain, the eyes, and their respective nerves. The inflammation associated with MS can damage myelin (the insulation that surrounds the nerves) and the actual nerves. This causes scarring in multiple damaged areas, lending to the name multiple sclerosis. Sclerosis is another term for hardening or scarring of tissue.
This damage disrupts information being sent to and from the brain through the nerves and leads to a wide variety of symptoms. Symptoms typically include difficulty walking, spasticity (i.e. stiffness or involuntary muscle spasms – typically in the legs), muscle weakness or numbness, tiredness, pain, cognitive problems, bladder and bowel issues, and changes in mood. These symptoms can be different for every patient and may change as time goes on.
MS is actually one of the more researched diseases regarding its relationship to CBD due to the drug approved in the EU, Sativex. This is the same drug as nabiximols in the U.S. and is currently an investigational product seeking FDA-approval. Sativex is a mouth spray that contains THC and CBD in a 1:1 ratio. It is indicated for treatment of moderate to severe spasticity associated with MS in those who have not responded well to other anti-spasmodic medications.
A lot of the data is valid and supports the use of CBD (with THC) in MS, especially regarding the symptom of spasticity. There is other data to help support its use with MS patients who also have pain or overactive bladder. For CBD alone, there is preclinical data to support CBD helping to decrease the immune system attacking itself and to reduce inflammation.

Summaries of CBD and Autoimmune Disease Studies
Below are some brief summaries of the studies that were reviewed for this article, as well as links to the articles for more in-depth information if you are curious. The search was focused on CBD and the respective autoimmune diseases specifically, however some of the studies look at other compounds in addition to CBD.
Psoriasis
This 2007 study was completed in cell culture and investigated the impact of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, on skin cells known as keratinocytes.
They found that the cannabinoids stopped the growth (or proliferation) of new skin cells. They also found that this did not happen through action on the cannabinoid receptors and speculated that it may be through other receptors, such as GPR55 or PPAR-γ.
The authors concluded that because cannabinoids can decrease the proliferation of skin cells, they could have therapeutic potential for psoriasis treatment.
Epigenetic control of skin differentiation genes by phytocannabinoids
This 2013 study was also performed in cell culture and looked at how cannabinoids may deal with genetic regulation of skin cells. The cannabinoids included CBD, CBG (cannabigerol), and CBDV (cannabidivarin). Specifically, the researchers looked at DNA methylation patterns when cannabinoids were introduced to keratinocytes. DNA methylation is a way that the body can turn off certain genes, which is commonly referred to as epigenetics.
The authors found that CBD and CBG could turn off certain genes that are associated with skin cell growth, but not CBDV. They also found that CBD acted through the CB1 receptor, whereas CBG did not act through the cannabinoid receptors. Additionally, CBD had more epigenetic action than CBG.
From this, the authors concluded that because both CBD and CBG affected the regulation of skin cell growth, they could be potential treatments for skin diseases. They mentioned that CBD may have more potential than CBG based off their findings.
Cannabidiol exerts sebostatic and antiinflammatory effects on human sebocytes
This 2014 study was also performed in cell culture and investigated how CBD could help with acne.
The authors found that CBD reduced sebum (or oil) production, reduced inflammation, and reduced skin cell proliferation. They also found that this happened through activation of TRPV4 ion channels and the anti-inflammatory actions occurred through the A2A receptor.
From this, the conclusion was that CBD may be an effective potential treatment for acne. Since the mechanism behind acne and the mechanism behind psoriasis are similar (i.e. they are both related to skin cell proliferation issues and inflammation), this also lends support to using CBD for psoriasis.
Lupus
This 2018 study was performed in cell culture and investigated the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in lupus.
They found that 2-arachidonoylglycerol (aka 2-AG, a type of endocannabinoid) levels were significantly increased in cells of lupus patients when compared to healthy cells. They also found some differences in enzymes that deal with 2-AG.
The authors conclude that their study suggests dysregulation of the ECS may play a role in lupus. They also stated that this is why cannabis-based medications should be researched more for their immune modulating properties.
This December 2018 study from Israel was done in mice and looked into the effects of CBD in lupus.
Interestingly, they found that CBD increased proteinuria in the mice with lupus when compared to the normal mice. Proteinuria is a way to measure kidney damage and it simply means there is excess protein spilling into the urine (which is typically not normal). Kidney damage is one of the many effects of lupus.
The authors conclude that CBD can enhance disease progression of lupus in mice, and therefore humans with lupus should utilize CBD with caution until more research is completed.
This recent 2019 study suggests gene mutations that involve 2-AG are associated with lupus. They believe that an overactive enzyme that breaks down 2-AG may limit the ability of the body to respond to infections.
This allows for potential of a genetic marker or biomarker that could help diagnose lupus. It could also provide some guidance for different mechanisms for possible treatment of lupus.
Multiple Sclerosis
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2011 trial was done in patients with MS who had not responded to other anti-spasmodic medications. They were given Sativex in addition to other spasticity medications.
The researchers used a Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) to measure the severity of spasticity in the patients. They found that the there was a significant difference in this score between the groups, with lower scores in the group receiving Sativex.
From this, the authors concluded that Sativex (in addition to other medications) was effective at reducing spasticity in MS patients. Of note, this study did not look at CBD by itself, but in combination with THC.
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2013 trial was done in patients with MS who did not have adequate responses to pain medications. They were given Sativex in addition to other pain medications.
The primary endpoint of this study was not significant. They compared responsiveness of medication in the Sativex group and the placebo group and found them to be similar. However, in the next phase of their trial they found that people had failed treatment faster in the placebo group than in the Sativex groups. They also found that the Sativex group had lower pain scores and higher sleep quality scores.
These results make sense because traditional pain medications are effective at reducing pain when first given, however patients begin to develop tolerance to them, and they start to not work as well for their pain. So, this supports the idea that Sativex could be a better option for chronic pain due to the time to treatment failure being longer in that group. Of note, this study did not look at CBD by itself, but in combination with THC.
Randomized controlled trial of Sativex to treat detrusor overactivity in multiple sclerosis.
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2010 trial was done in patients with MS who also had overactive bladder (OAB). They were given Sativex in addition to other bladder medications.
Their primary endpoint, reduction in daily number of urinary incontinence episodes, was not significant. However, other symptoms such as nocturia (waking up and needing to urinate at night) and number of voids per day were significant in favor of Sativex.
The authors concluded that although their primary endpoint was not significant, Sativex did have a positive impact on the symptoms associated with OAB and may provide some use for bladder dysfunction in MS patients. Of note, this study did not look at CBD by itself, but in combination with THC.
This 2015 study was performed in mice and sought out to see if CBD could help with MS-induced apoptosis (self-killing of cells).
They found that CBD did impact mediators involved with apoptosis. They also found that there was not formation of apoptotic bodies in the spine.
From this, the authors concluded that this provides a different mechanism behind how CBD alone can help with MS through its “anti-apoptotic power”.
This 2013 study utilized a viral model of MS to determine if CBD can protect against the harmful effects of inflammation associated with this disease.
They found that CBD decreased pro-inflammatory mediators and decreased the number of other harmful mediators involved with inflammation. They also found that the A2A adenosine receptor was involved in the anti-inflammation mechanism.
The authors concluded that CBD has anti-inflammatory effects that can have significant potential in treating MS.
How Valid is the Research?
It is important to keep in mind that for CBD use in psoriasis and lupus, as with most topics surrounding CBD, most of the research is preclinical or anecdotal evidence due to it being performed in animal models or cell culture. This means that it is not definitive by any means but is hypothesis-generating. It allows for more specific research to be conducted and eventually clinical trials to be completed. Data shows great promise for psoriasis, however with lupus the data is conflicting and CBD use should be done with caution.
The research surrounding CBD and MS is actually different than other research regarding CBD. It has more data in humans, and clinical trials that are the golden standard of randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. With this, the data supporting the use of CBD and MS is valid and can be used more confidently to give suggestions regarding MS.
However, the data in humans is using a combination of THC and CBD, and not just CBD alone. And, the concentration of the THC well exceeds the federal limit on current CBD products of 0.3%. Therefore, CBD products should not be mistaken for the equivalent of the product tested in these trials. The other research with just CBD was only in animals or cell culture, and therefore it is harder to say with certainty that CBD alone is effective for MS, although the data is promising.
It is always best practice to talk with a health care professional before using CBD to help with any health conditions you may have. They can help you evaluate the research and decide if it is the best option for you. They can also help you determine if any drug interactions exist with any current medications you might be taking and give suggestions for how to avoid them.
Looking to the Future
Autoimmune diseases come in a wide variety of forms, but they have a common linker – inflammation. CBD is known to be anti-inflammatory and because of this, it may help with most autoimmune diseases.
There is a lot of research to support CBD, in combination with THC, in treating symptoms associated with MS. We will just have to wait and see if this drug product gets approval from the FDA. There is also a lot of promise for CBD with other autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis.
As more people turn to CBD for its anti-inflammation properties, we may see more data supporting its potential use as treatment for autoimmune diseases.
References:
- http://www.autoimmuneregistry.org/autoimmune-statistics
- https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.aarda.org/knowledge-base/common-autoimmune-diseases/
- https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/autoimmune/index.cfm
- https://medlineplus.gov/autoimmunediseases.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC20965/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC16904/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5022003/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1472541/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3371734/
- https://www.aad.org/media/news-releases/topical-cannabis
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17157480
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3791996/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4151231/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=29655919
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=cannabidiol+lupus
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30728209
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00681538
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23180178
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20829244
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26744883
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23851307
Dr. Irene Zollars (Pharm D/MBA)
Latest posts by Dr. Irene Zollars (Pharm D/MBA) (see all)
- FAB CBD Review - November 26, 2019
- Is CBD The Answer to Autoimmune Diseases? - March 7, 2019
- Can CBD Heal the Brain? - February 21, 2019









